Space Missions Every Space Lover Should Know
Share
Did you know the Kármán line, marking space's edge, is only 62 miles (100 kilometers) up? This fact kicks off the amazing journey of space exploration. It's a story of incredible achievements and discoveries, from the Space Race to NASA's missions.
We'll dive into key space missions that every space fan should know. We'll see the Apollo missions that took humans to the Moon. We'll also explore Mars missions, like Curiosity, and the International Space Station, a symbol of global teamwork.
Additionally, we'll examine the Space Shuttle program and the Hubble Space Telescope. We'll look ahead to NASA's Artemis program and SpaceX's innovative space travel ideas.
The Space Race: USSR vs. USA
The Space Race was a fierce competition between the United States and the Soviet Union. It started in the mid-20th century and ended with major milestones in space exploration. Both countries invested heavily in their space programs, leading to quick advancements in technology and human spaceflight.
Sputnik 1: The First Artificial Satellite
The Space Race began on October 4, 1957, with the Soviet Union launching Sputnik 1. This was the world's first artificial satellite. It shocked the United States and made them want to catch up with their Cold War rival. Sputnik 1 orbited the Earth once every 96 minutes, starting the space exploration era.
Yuri Gagarin: The First Human in Space
On April 12, 1961, Yuri Gagarin became the first human to orbit the Earth. He completed one full orbit in 108 minutes aboard Vostok 1. Gagarin's flight was a big win for the Soviet Union and a setback for the United States. It showed that humans could go to space and opened the door for future missions.
Alan Shepard: The First American in Space
The United States responded to Gagarin's achievement by sending Alan Shepard into space on May 5, 1961. Shepard's suborbital flight lasted about 15 minutes and reached an altitude of 116 miles. Although it was not as impressive as Gagarin's, it marked the start of the United States' manned space program.
| Mission | Country | Date | Achievement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sputnik 1 | USSR | October 4, 1957 | First artificial satellite |
| Vostok 1 | USSR | April 12, 1961 | First human in space (Yuri Gagarin) |
| Mercury-Redstone 3 | USA | May 5, 1961 | First American in space (Alan Shepard) |
| Vostok 6 | USSR | June 16, 1963 | First woman in space (Valentina Tereshkova) |
The Space Race continued in the 1960s, with both sides making big strides in space exploration. The competition ended with the United States' Apollo 11 mission. This mission landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969, ending the Space Race.
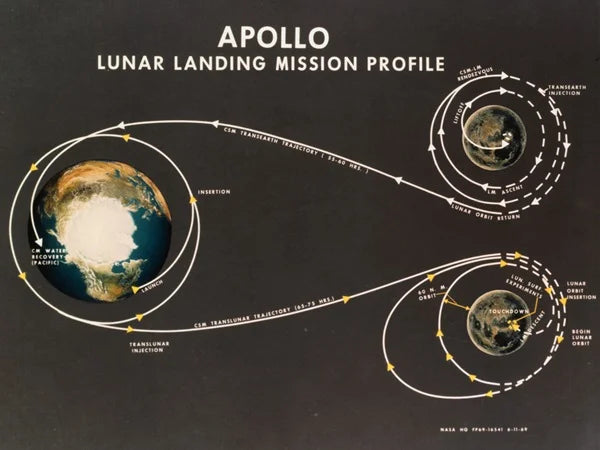
The Apollo Missions: Landing on the Moon
The Apollo missions were a series of groundbreaking space missions by NASA. They aimed to land humans on the moon and bring them back safely. From 1969 to 1972, six manned Apollo missions successfully achieved this goal. They landed in the moon's equatorial regions, all on the side facing Earth.
The Apollo missions were a huge step for humanity, showing we could explore beyond Earth. Their success came from years of research and the hard work of many people involved.
Apollo 11: The First Moon Landing
The Apollo 11 mission, launched on July 16, 1969, was the first to land humans on the moon. On July 20, 1969, the lunar module Eagle landed on the moon's surface. Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to walk on another celestial body.
Millions watched worldwide as Armstrong descended the ladder and said, "That's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind." Aldrin joined him soon after. Together, they spent over two hours outside, collecting samples and conducting experiments.
Neil Armstrong: The First Man on the Moon
Neil Armstrong was born on August 5, 1930, in Wapakoneta, Ohio. He was an American astronaut and aeronautical engineer. As the commander of Apollo 11, he became the first person to walk on the moon.
"I believe that every human has a finite number of heartbeats. I don't intend to waste any of mine." - Neil Armstrong
Before becoming an astronaut, Armstrong was a naval aviator and test pilot. His experience made him a great choice for the Apollo program. His leadership during Apollo 11 was key to its success.
| Mission | Launch Date | Landing Date | Crew |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apollo 11 | July 16, 1969 | July 20, 1969 | Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin, Michael Collins |
| Apollo 12 | November 14, 1969 | November 19, 1969 | Charles "Pete" Conrad, Alan Bean, Richard Gordon |
| Apollo 14 | January 31, 1971 | February 5, 1971 | Alan Shepard, Edgar Mitchell, Stuart Roosa |
| Apollo 15 | July 26, 1971 | July 30, 1971 | David Scott, James Irwin, Alfred Worden |
| Apollo 16 | April 16, 1972 | April 21, 1972 | John Young, Charles Duke, Ken Mattingly |
| Apollo 17 | December 7, 1972 | December 11, 1972 | Eugene Cernan, Harrison Schmitt, Ronald Evans |
The Space Shuttle Program: Reusable Spacecraft
NASA's space shuttle program ran from 1981 to 2011. It was a big step in space exploration. The goal was to make spacecraft that could go back to Earth, making space travel cheaper and more frequent.
Over 30 years, the program flew 135 missions with five shuttles: Columbia, Challenger, Discovery, Atlantis, and Endeavour. These missions helped build the International Space Station and launched the Hubble Space Telescope. They were key achievements.
But, the program faced tough times and tragedies. On January 28, 1986, Challenger exploded just 73 seconds into its flight. All seven crew members lost their lives. Then, on February 1, 2003, Columbia broke apart during re-entry, killing seven more astronauts. These disasters made NASA rethink safety and pause shuttle flights.
The space shuttle program has taught us incredible things about the capabilities of our astronauts and our technology. It's enabled us to do things that we could never have done without it. - Ellen Ochoa, former NASA astronaut and director of the Johnson Space Center
Despite the setbacks, the space shuttle program was a huge success. It greatly advanced our space knowledge and ability to explore. Its legacy inspires scientists, engineers, and space fans to this day.
| Space Shuttle | First Flight | Last Flight | Number of Missions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Columbia | April 12, 1981 | February 1, 2003 | 28 |
| Challenger | April 4, 1983 | January 28, 1986 | 10 |
| Discovery | August 30, 1984 | March 9, 2011 | 39 |
| Atlantis | October 3, 1985 | July 21, 2011 | 33 |
| Endeavour | May 7, 1992 | June 1, 2011 | 25 |
As we explore space further, we must remember the space shuttle program's lessons. Building on its successes and learning from its failures will help us achieve more. It will inspire future generations to dream big and reach for the stars.
The International Space Station: A Global Collaboration
The International Space Station (ISS) is a symbol of global teamwork in space. It's a joint effort by five space agencies from 15 countries. NASA, Roscosmos, JAXA, ESA, and CSA are all part of it. Since November 2000, it has been home to humans in space, making it the longest stay.
The ISS floats 250 miles above Earth, perfect for space research. Right now, nine people live and work there. They include NASA astronauts and cosmonauts from Russia, and even crew from Boeing's Starliner.
ISS Construction and Assembly
The ISS started building in 1998 with the launch of Zarya. More parts were added over time, thanks to space shuttles and rockets. The building stopped in 2011, when the Space Shuttle program ended.
The ISS is huge, measuring 354 feet wide and 243 feet long. It has a lot of space, over 35,000 cubic feet. It can hold up to seven astronauts at a time.
| ISS Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Mass | 450,000 kg (990,000 lb) |
| Length | 109 m (358 ft) overall, 94 m (310 ft) truss |
| Width | 73 m (239 ft) solar array |
| Pressurized Volume | 1,005.0 m³ (35,491 cu ft) |
| Altitude | Perigee: 413 km (256.6 mi), Apogee: 422 km (262.2 mi) |
| Orbital Inclination | 51.64° |
| Orbital Speed | 7.67 km/s; 27,600 km/h; 17,100 mph |
| Orbital Period | 92.9 minutes |
| Orbits per Day | 15.5 |
Landmark Experiments and Discoveries on the ISS
The ISS has seen many important experiments and discoveries. The microgravity environment is perfect for research that can't be done on Earth. Some key areas include:
- Human physiology and the effects of long-duration spaceflight on the human body
- Materials science, including the development of new materials and manufacturing techniques
- Plant growth and space agriculture
- Earth observation and remote sensing
- Astronomical observations and space physics
By March 2024, 279 people from 22 countries had visited the ISS. This includes 13 private visitors. NASA astronauts have made many trips, with some visiting up to five times.
"The International Space Station is a unique laboratory that allows us to conduct cutting-edge research and push the boundaries of our understanding of the universe. It is a testament to the power of global collaboration in the pursuit of scientific knowledge and space exploration." - NASA Administrator
The ISS will keep working until 2030, helping us learn more about space. By October 1, 2024, it will have been in space for 25 years, 10 months, and 11 days. It will have orbited Earth 141,117 times.
Mars Exploration: The Red Planet
Mars, the red planet, has fascinated humans for centuries. Recently, Mars exploration has become a major focus in space missions. NASA's Mars Exploration Program leads this effort, sending various spacecraft to study the Martian surface and atmosphere.
Since 1997, Mars has been a constant focus of exploration. Orbiters, landers, and rovers have been sent to study the planet. NASA has had a presence on Mars every day for the last 20 years, captivating the public.
Mars Rovers: Spirit, Opportunity, and Curiosity
The Mars rovers Spirit and Opportunity were launched in 2003. They were meant to last 90 days but kept exploring for years. Spirit worked until 2010, and Opportunity lasted 15 years until 2018. They found evidence of past water on Mars.
The Curiosity rover, launched in 2011, has been a major breakthrough. It has shown that Mars could have supported life in the past. Curiosity's discoveries are helping plan future missions to find signs of ancient life.
| Rover | Launch Year | Mission Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Spirit | 2003 | 2004-2010 |
| Opportunity | 2003 | 2004-2018 |
| Curiosity | 2011 | 2012-Present |
Future Mars Missions: Perseverance Rover and Ingenuity Helicopter
The Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter were launched in 2020. Perseverance is searching for signs of life and collecting samples. Ingenuity made history with the first flight on another planet.
NASA's Mars Sample Return mission is planned to cost $10 billion. It aims to bring Martian samples back to Earth. Other space agencies also have big plans for Mars.
"The robotic exploration of Mars by NASA has engaged the public imagination successfully. The public consumed new media content constantly, accessing images and stories related to Mars exploration."
As we explore Mars, our understanding of the planet will grow. These missions are preparing us for future human exploration. The search for life on Mars is an exciting journey in space exploration.
Groundbreaking Space Missions
Space exploration has led to many groundbreaking missions. These missions have greatly expanded our knowledge of the universe. They have also captured the hearts of people worldwide.
Voyager 1 and 2: Exploring the Outer Solar System
The Voyager missions were launched in 1977. They have explored the outer solar system. Voyager 1 and 2 have given us detailed images and data of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, and their moons.
These spacecraft have also studied the outer reaches of our solar system. Voyager 1 became the first human-made object in interstellar space in 2012.
Hubble Space Telescope: Unveiling the Universe
The Hubble Space Telescope was launched in 1990. It has changed how we see the universe. It has captured stunning images of distant galaxies and nebulae.
Hubble has also helped us understand where new stars are born. It has shown us the beauty of the cosmos.
"The Hubble Space Telescope has been one of the most transformative scientific instruments ever built, providing a window into the universe that has changed our understanding of its vastness and beauty."
Cassini-Huygens: Exploring Saturn and Its Moons
The Cassini-Huygens mission was a joint effort by NASA, ESA, and ASI. It studied Saturn and its moons from 2004 to 2017. The mission revealed the complexity of Saturn's moons, like Titan and Enceladus.
Cassini's findings have opened up new possibilities for life beyond Earth. They have greatly expanded our knowledge of the outer solar system.
| Mission | Launch Year | Key Discoveries |
|---|---|---|
| Voyager 1 & 2 | 1977 | Detailed images and data of outer solar system planets and moons |
| Hubble Space Telescope | 1990 | Stunning images of galaxies, nebulae, and stellar nurseries |
| Cassini-Huygens | 1997 | Comprehensive study of Saturn and its moons, revealing their complexity |
These missions have greatly expanded our scientific knowledge. They have also inspired a new generation of space enthusiasts. The Voyager missions, the Hubble Space Telescope, and Cassini-Huygens will continue to guide future discoveries in space exploration.
SpaceX: Revolutionizing Space Exploration
Elon Musk founded SpaceX in 2002. It has changed how we explore space. SpaceX made launching things into orbit cheaper with reusable rockets.
The Falcon 9 rocket is a key part of SpaceX. It has sent cargo and crew to the International Space Station (ISS). In 2020, SpaceX launched the first crewed commercial spacecraft, Crew Dragon, to the ISS.
SpaceX is working on the Starship. It's a reusable spacecraft for trips to the Moon, Mars, and more. The goal is to help humans live on other planets.
"I think it is important for humanity to become a spacefaring civilization and a multi-planet species. It's going to take a lot of resources to build a city on Mars. I want to be able to contribute as much as possible to the city on Mars. That means just a lot of capital." - Elon Musk, CEO and Founder of SpaceX
SpaceX also launched Starlink for fast internet worldwide. Over 6,000 small satellites are in orbit as of April 2024. Starlink is changing how we connect globally.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| SpaceX Revenue (2022) | US$4.6 billion |
| SpaceX Net Income (2022) | US$−559 million |
| Number of Employees (September 2023) | 13,000+ |
| Company Valuation (June 2024) | US$200 billion |
| Starlink Satellites in Orbit (April 2024) | 6,000+ |
| Falcon 9 Rocket Launches and Landings (June 2024) | 300+ |
SpaceX is changing space exploration. Its impact on the industry and the world is huge. With new technologies and a big vision, SpaceX is leading us to a multi-planetary future.
Future Space Missions: What's Next?
Looking ahead, many exciting space missions are coming. They will help us learn more about the universe and explore new places. These missions will take us back to the Moon and search for life on other planets.
NASA's Artemis Program: Returning to the Moon
NASA's Artemis program aims to send humans back to the Moon by 2024. The goal is to make a lasting presence on the Moon. This will be a big step towards going to Mars and beyond.
The program includes many missions. It will use the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft. It will also build the Lunar Gateway, a space station in lunar orbit.
James Webb Space Telescope: Successor to Hubble
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) was launched in 2021. It's the biggest and most powerful space telescope ever made. Its mirror is 6.5 meters wide, allowing it to see the universe in great detail.
The JWST will study the early universe and how galaxies form. It will also look at the atmospheres of planets outside our solar system. It can see through cosmic dust and gas to observe distant objects.
Mission to Europa: Searching for Life on Jupiter's Moon
NASA plans to send a mission to Europa, a moon of Jupiter. The mission will check if Europa can support life. Europa has a liquid ocean beneath its ice, making it a prime candidate for life.
The Europa Clipper mission will fly by Europa in the 2020s. It will study the moon's surface and ocean to see if it can support life.
Europa, one of Jupiter's moons, has a liquid, salty water ocean beneath a layer of ice, making it a top candidate to support life. The Europa Clipper mission will explore this intriguing world and investigate whether it has the right conditions for life to exist.
| Mission | Agency | Launch Date | Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artemis 1 | NASA | 2022 | Uncrewed test flight of SLS and Orion |
| James Webb Space Telescope | NASA, ESA, CSA | 2021 | Infrared space observatory |
| Europa Clipper | NASA | 2020s | Study habitability of Europa |
These missions are just a few of the exciting plans for space exploration. As we explore more, we'll make new discoveries and achieve amazing things.
The Importance of Space Exploration
Space exploration has led to amazing technological advancements that change our lives. It helped create the Global Positioning System (GPS), solar panels, and emergency beacons. These innovations improve our lives, boost the economy, and create jobs.
Space exploration also drives scientific discovery. It helps us understand our place in the universe and the origins of life. Space missions have made major discoveries in biology, medicine, and physics. They satisfy our curiosity and expand our knowledge.
Exploring space also brings nations together. Countries work together to achieve goals and explore new frontiers. This cooperation builds trust, diplomacy, and a shared purpose among countries.
Most importantly, space exploration inspires young people to study science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). It sparks their imagination and encourages them to dream big. The pursuit of space shows our ingenuity, perseverance, and desire to explore the unknown.
Source Links
- https://www.astronomy.com/space-exploration/15-things-kids-should-know-about-space/ - 15 things kids should know about space travel | Astronomy.com
- https://www.nasa.gov/learning-resources/for-students-grades-k-4/ - For Students Grades K-4 - NASA
- https://www.mos.org/discover/article/spacing-out/whats-happening-in-2024 - What’s Happening in Space in 2024?
- https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/history-space-exploration/ - The History of the Space Race
- https://www.britannica.com/science/space-exploration/Crewed-spaceflights-1990-99 - Space exploration - Astronauts, Missions, Decade
